HA-RDet on Google Earth
Abstract
Oriented object detection in aerial images poses a significant challenge due to their varying sizes and orientations. Current state-of-the-art detectors typically rely on either two-stage or one-stage approaches, often employing Anchor-based strategies, which can result in computationally expensive operations due to the redundant number of generated anchors during training. In contrast, Anchor-free mechanisms offer faster processing but suffer from a reduction in the number of training samples, potentially impacting detection accuracy. To address these limitations, we propose the Hybrid-Anchor Rotation Detector (HA-RDet), which combines the advantages of both anchor-based and anchor-free schemes for oriented object detection. By utilizing only one preset anchor for each location on the feature maps and refining these anchors with our OrientationAware Convolution technique, HA-RDet achieves competitive accuracies, including 75.41 mAP on DOTA-v1, 65.3 mAP on DIOR-R, and 90.2 mAP on HRSC2016, against current anchor-based state-of-the-art methods, while significantly reducing computational resources.
Method
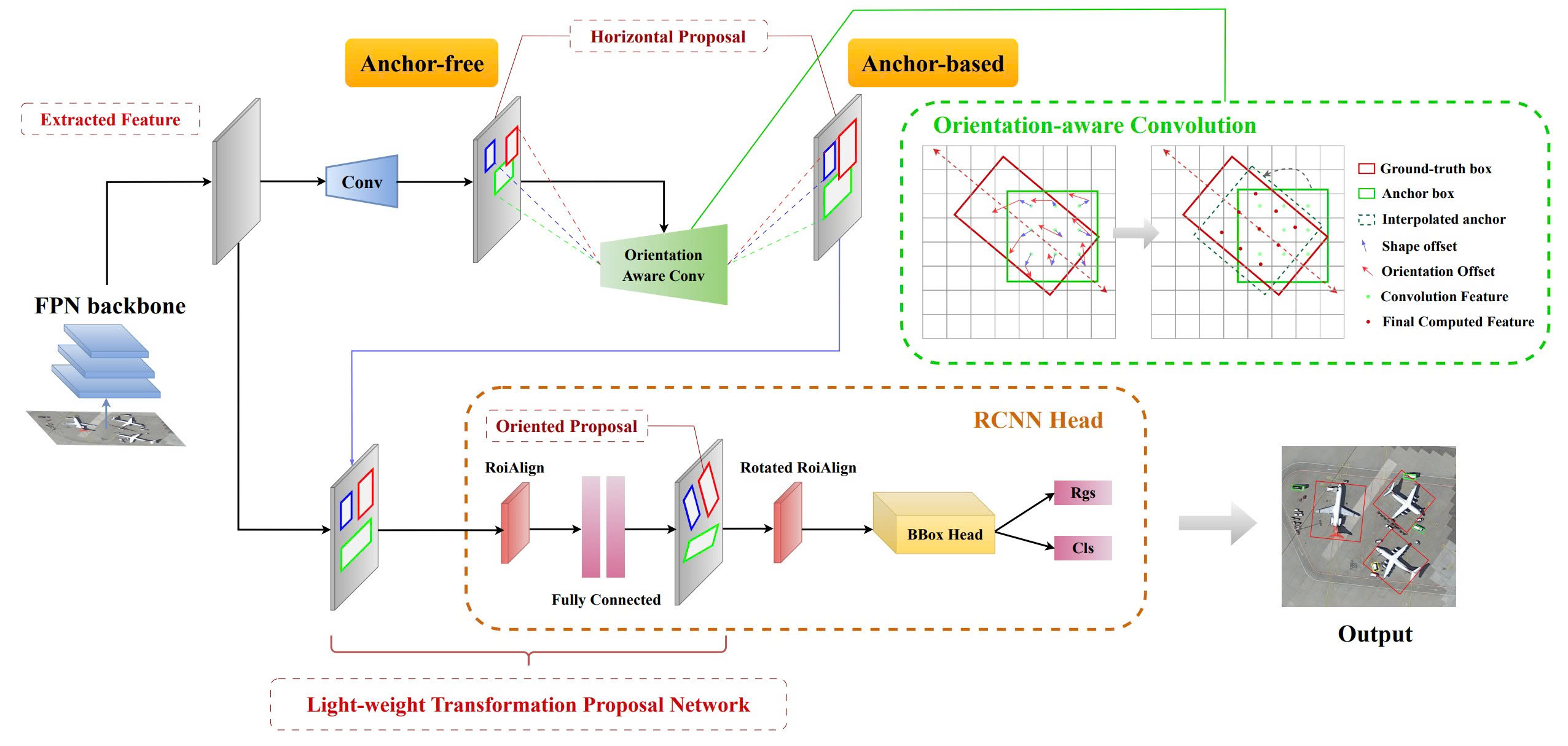
Illustration of the architecture of the proposed HA-RDet. At first, an aerial image is passed through the FPN backbone to extract deep features. Then, the extracted features are fed through the Hybrid-Anchor RPN to produce horizontal anchors via an Anchor-free assigner strategy on rectangularized oriented ground truths. The anchors are refined with the novel Orientation-aware Convolution and the later Anchor-based head to produce high-quality horizontal proposals. After that, the lightweight proposal transformation network learns to produce oriented proposals from predicted RoI Align processed horizontal proposals. Finally, these oriented proposals are refined through oriented bounding box heads for classification and bounding box regression.
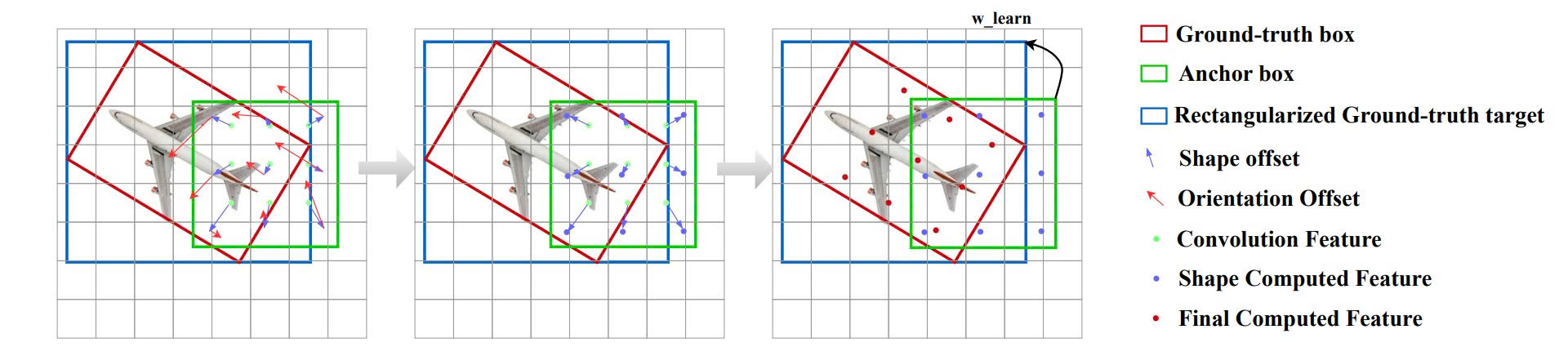
The shape offsets are computed via anchor size; ground-truth orientation is adopted to perform orientation offsets calculation. Shape offsets and orientation offsets produce the final features used for training the Anchor-based refinement stage. The final computed features are orientation-awareness, surging HA-RDet performance significantly.
DOTA, DIOR-R HRSC Benchmarks
BibTeX
@article{nguyen2024ha,
title={HA-RDet: Hybrid Anchor Rotation Detector for Oriented Object Detection},
author={Nguyen, Phuc DA},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2412.14379},
year={2024}
}